 BIO、NIO、AIO、Netty
BIO、NIO、AIO、Netty
# 前言
o操作分为两部分,发起io请求,和io数据读写。阻塞、非阻塞主要是针对线程发起io请求后,是否立即返回来定义的,立即返回称为非阻塞io,否则称为阻塞io。 同步、异步主要针对io数据读写来定义的,读写数据过程中不阻塞线程称为异步io,否则,称为同步io。
提示
- BIO:同步阻塞IO
- NIO:同步非阻塞IO
- AIO:异步非阻塞IO
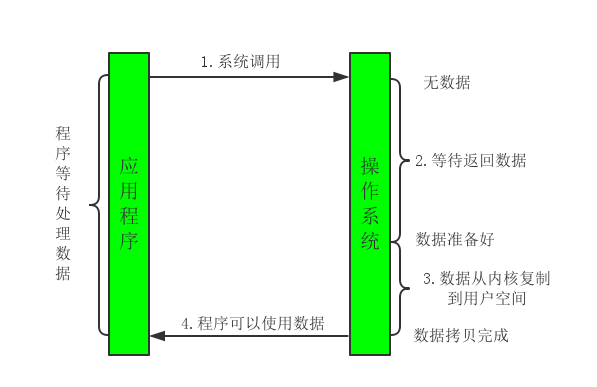
- BIO **线程发起io请求后,一直阻塞(阻塞io),直到数据就绪后,用户线程将数据写入socket空间,或从socket空间读取数据(同步)。 **
# 服务端
package com.xiangxue.io.bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* BIO 模型, 服务端
*/
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ServerSocket
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket();
//绑定 地址
ss.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));
//这里用 while(true) 是为了可以 接收多个客户端连接
while(true) {
Socket s = ss.accept(); //阻塞方法,如果没有客户端连接,将一直阻塞
//这里为什么要开启线程呢?
new Thread(() -> {
handle(s);
}).start();
}
}
/**
* 具体得处理方法, 处理客户端连接数据,并将数据返回给客户端(使用 OutPutStream)
* @param s
*/
static void handle(Socket s) {
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = s.getInputStream().read(bytes); // 方法阻塞,知道读取完成才会执行下面的代码, 造成了大量线程处于休眠状态,只能等待输入/输出数据就绪;
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
s.getOutputStream().write(bytes, 0, len);// 将数据写回客户端
s.getOutputStream().flush();//刷新输出流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# 客户端
package com.xiangxue.io.bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
s.getOutputStream().write("HelloServer".getBytes());
s.getOutputStream().flush();
//s.getOutputStream().close();
System.out.println("write over, waiting for msg back...");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = s.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
s.close();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# NIO
线程发起io请求后,立即返回(非阻塞io)。用户线程不阻塞等待,但是会又一个 Selector线程 轮询检查数据是否就绪,当数据就绪后,用户线程将数据从用户空间写入socket空间,或从socket空间读取数据到用户空间(同步)
| 核心组件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| 1、缓冲区buffer | 负责存储 可以保存多个相同类型的数据 |
| 2、通道channel | 负责传输 表示io源于目标打开的连接 channel不能直接访问数据,只能与buffer进行交互 |
| 3、选择器selector | 单线程 利用selector可以使一个单独的线程管理多个Channel通道,选择器selector是非阻塞的核心 |

# 服务端
package com.xiangxue.io.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// ServerSocketChannel的初始化
//创建通道, 这个和BIO的 InputStream 、OutputStream 区别在于, channel 是双向的
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));
//设置为非阻塞
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("server started, listening on :" + ssc.getLocalAddress());
//创建通道管理器, 通过轮询的方式 检测通道时候有客户端连接,如果有客户端连接,则 进行相应的处理
// Selector的初始化
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 将Selector(通道管理器) 和 通道进行绑定,并注册 OP_ACCEPT 事件
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);// 注册客户端连接事件
while(true) {
selector.select();// 如果有客户端连接,则该方法会返回,如果没有客户端连接,则该方法会一直阻塞
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); // selector获取到所有的 连接 key
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {// 遍历所有的链接 key
SelectionKey key = it.next();
it.remove();
handle(key); // 对客户端的链接进行 相应的处理
}
}
}
private static void handle(SelectionKey key) { // SelectionKey 中封装了 客户端的一些信息
if(key.isAcceptable()) { // 如果客户端是连接状态
try {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); // 在上面的方法中 selector 已经和 channel 想绑定,所以可以获取到相应的 channel
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); // 再次判断通道 有客户端进入,并且连接
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ ); // 将通道中注册 数据读取事件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
} else if (key.isReadable()) { //如果是 有数据传递过来的状态
SocketChannel sc = null;
try {
sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512); // 创建读取的缓冲区 ByteBuffer
buffer.clear();
int len = sc.read(buffer);
if(len != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));
}
ByteBuffer bufferToWrite = ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes());
sc.write(bufferToWrite); //将消息回送给客户端
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sc != null) {
try {
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
# 线程池版服务端
package com.xiangxue.io.nio;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class PoolServer {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50);
private Selector selector;
//中文测试
/**
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PoolServer server = new PoolServer();
server.initServer(8000);
server.listen();
}
/**
*
* @param port
* @throws IOException
*/
public void initServer(int port) throws IOException {
//
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//
this.selector = Selector.open();
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务端启动成功!");
}
/**
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void listen() throws IOException {
// 轮询访问selector
while (true) {
//
selector.select();
//
Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
//
ite.remove();
//
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//
SocketChannel channel = server.accept();
//
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
//
key.interestOps(key.interestOps()&(~SelectionKey.OP_READ));
//
pool.execute(new ThreadHandlerChannel(key));
}
}
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param
* @throws IOException
*/
class ThreadHandlerChannel extends Thread{
private SelectionKey key;
ThreadHandlerChannel(SelectionKey key){
this.key=key;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
int size = 0;
while ((size = channel.read(buffer)) > 0) {
buffer.flip();
baos.write(buffer.array(),0,size);
buffer.clear();
}
baos.close();
//
byte[] content=baos.toByteArray();
ByteBuffer writeBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(content.length);
writeBuf.put(content);
writeBuf.flip();
channel.write(writeBuf);//
if(size==-1){
channel.close();
}else{
//
key.interestOps(key.interestOps()|SelectionKey.OP_READ);
key.selector().wakeup();
}
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
# 客户端
客户端同 BIO的客户端
# AIO
线程发起io请求后,立即返回(非阻塞io),当数据读写完成后,OS通知用户线程(异步)。这里数据写入socket空间,或从socket空间读取数据到用户空间由OS完成,用户线程无需介入,所以也就不会阻塞用户线程,即异步。 
# 服务端
package com.xiangxue.io.aio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建 AIO 通道, 绑定地址端口
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888));
//等待客户端连接, 通过事件的方式,也就是回调函数的方式, 客户端连接之后,立即返回
serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel client, Object attachment) {
serverChannel.accept(null, this); //这里必须,不然后续来的客户端进入
try {
System.out.println(client.getRemoteAddress());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 读取客户端数据
client.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
//读取完成
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
attachment.flip();
System.out.println(new String(attachment.array(), 0, result));
client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes()));
}
//数据读取失败
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//当操作失败的时候回调
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
while (true) { //这里是让服务端等待客户端的连接,不然会直接执行完成
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 线程池版 服务端
package com.xiangxue.io.aio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ServerWithThreadGroup {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 1);
//中文测试
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup)
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888));
serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel client, Object attachment) {
serverChannel.accept(null, this);
try {
System.out.println(client.getRemoteAddress());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
client.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
attachment.flip();
System.out.println(new String(attachment.array(), 0, result));
client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# 客户端
同BIO 客户端
AIO 区别于 NIO 的是 AIO 放弃了 Selector 轮询机制, 因为轮询会消耗CPU的资源, 而是使用 异步事件通知机制,如果数据准备就绪 则告诉客户端数据成功,可以获取数据 AIO基于时间驱动思想,采用proactor模式。数据完成后,由os主动通知应用程序,通过epoll实现,节省了NIO中selector循环遍历检测数据就绪的资源开销。同时,数据copy操作(用户空间<->socket空间)是由os完成的,无需应用程序参与,大大提高应用程序效率。
# Netty
Netty是一个基于NIO的并发框架。使用Netty可以搭建高负载的服务器,通过有限的线程去处理大量的连接。
# Netty 服务器
package com.xiangxue.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeListener;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloNetty {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new NettyServer(8888).serverStart();
}
}
class NettyServer {
int port = 8888;
public NettyServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void serverStart() {
//两个线程池
// bossGroup 只负责 客户端的连接
//具体的处理在 workerGroup (工人线程池)
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//处理客户端连接的线程池
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//工人线程池
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();//服务端启动必备,服务器启动类
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 制定NIO通道 通过反射工厂反射获得 (注意 这里使用的是 NioServerSocketChannel 区别于 客户端 )
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
//添加通道监听处理器
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//.pipeline() 相当于一个管道链或者事件链
ch.pipeline().addLast(new Handler()); // 向管道中添加 执行器
/// 这里 可以在上面声明一个 Handler ,因为加了 Sharable 注解,所以可以共用一个
}
});
try {
//b.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port));// 也可以使用这个方式绑定端口
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();// 同步绑定服务器监听端口
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); //同步 关闭通道
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭 两个线程池
try {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//通道处理器
//通过 Sharable 注解,指定当前Handler 可以在多个 channel 中共享 ,如果加了这个注解,这个Handler就不能有线程不安全的成员变量
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
class Handler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* @param ctx 通道上下文环境
* @param msg 客户端传过来的来的 数据
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
System.out.println("server: channel read");
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ctx.writeAndFlush(msg); // 将数据回写 到客户端
//ctx.close(); // 如果这里不关闭,客户端可以一直想服务器发送消息
//buf.release();
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER) // flush 所有的数据
// .addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);// 当flush后,关闭连接
}
/**
* 处理过程中的异常处理
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close(); //关闭通道
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
# Netty 客户端
package com.xiangxue.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Client().clientStart();
}
private void clientStart() {
// 创建线程池
EventLoopGroup workers = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(workers) //将线程池和 Bootstrap 进行绑定
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class) //使用Nio 模型通道
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channel initialized!");
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
try {
System.out.println("start to connect...");
//绑定服务器端口
ChannelFuture f = b.connect("127.0.0.1", 8888).sync();//.sync 阻塞连接过程, 直到连接完成
//阻塞, 直到通道关闭
//f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//workers.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
//ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
class ClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channel is activated.");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 向服务器发送数据
ChannelFuture f = null;
while (true) {// 这里是客户端一直发送消息到服务器,保持一个长连接的状态, 前提是 服务器的 ChannelHandlerContext(通道上下文) 不关闭
f = ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(scanner.next(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// 给数据传送成功,添加回调函数
f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
System.out.println("msg send!");
//ctx.close();
}
});
}
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println(byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
// 异常监听
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2022/03/08, 00:59:33