 Redis
Redis
# Redis 简介
【视频】项目实战-iToken-数据缓存服务-Redis 简介
# 什么是 Redis
Redis 是用 C 语言开发的一个开源的高性能键值对(key-value)数据库。它通过提供多种键值数据类型来适应不同场景下的存储需求,目前为止 Redis 支持的键值数据类型如下:
字符串类型 散列类型 列表类型 集合类型 有序集合类型
# Redis 的应用场景
缓存(数据查询、短连接、新闻内容、商品内容等等) 分布式集群架构中的 session 分离 聊天室的在线好友列表 任务队列(秒杀、抢购、12306 等等) 应用排行榜 网站访问统计 数据过期处理(可以精确到毫秒)
# Redis HA 方案
# 概述
HA(High Available,高可用性群集)机集群系统简称,是保证业务连续性的有效解决方案,一般有两个或两个以上的节点,且分为活动节点及备用节点。通常把正在执 行业务的称为活动节点,而作为活动节点的一个备份的则称为备用节点。当活动节点出现问题,导致正在运行的业务(任务)不能正常运行时,备用节点此时就会侦测到,并立即接续活动节点来执行业务。从而实现业务的不中断或短暂中断。
Redis 一般以主/从方式部署(这里讨论的应用从实例主要用于备份,主实例提供读写)该方式要实现 HA 主要有如下几种方案:
- keepalived: 通过 keepalived 的虚拟 IP,提供主从的统一访问,在主出现问题时, 通过 keepalived 运行脚本将从提升为主,待主恢复后先同步后自动变为主,该方案的好处是主从切换后,应用程序不需要知道(因为访问的虚拟 IP 不变),坏处是引入 keepalived 增加部署复杂性,在有些情况下会导致数据丢失
- zookeeper: 通过 zookeeper 来监控主从实例, 维护最新有效的 IP, 应用通过 zookeeper 取得 IP,对 Redis 进行访问,该方案需要编写大量的监控代码
- sentinel: 通过 Sentinel 监控主从实例,自动进行故障恢复,该方案有个缺陷:因为主从实例地址( IP & PORT )是不同的,当故障发生进行主从切换后,应用程序无法知道新地址,故在 Jedis2.2.2 中新增了对 Sentinel 的支持,应用通过 redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool.getResource() 取得的 Jedis 实例会及时更新到新的主实例地址
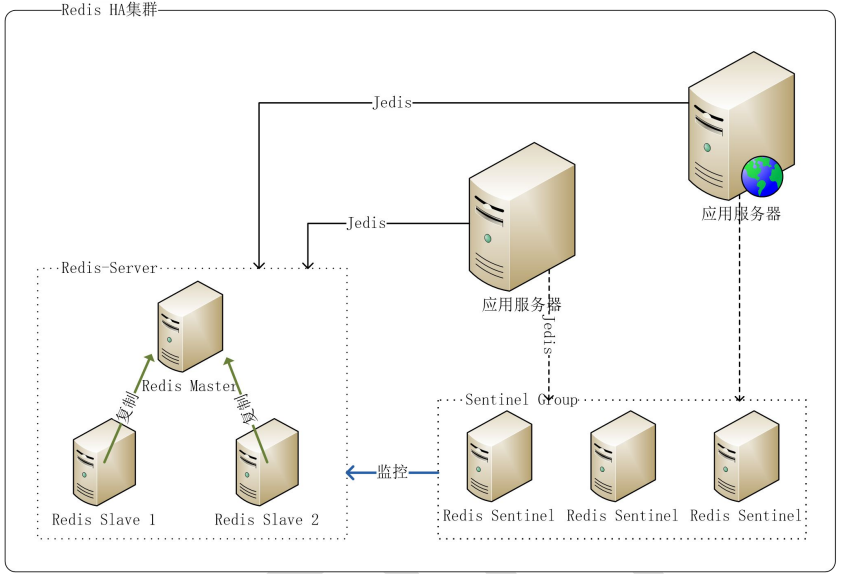 注意: sentinel 是解决 HA 问题的,cluster 是解决主从复制问题的,不重复,并且经常一起用
注意: sentinel 是解决 HA 问题的,cluster 是解决主从复制问题的,不重复,并且经常一起用
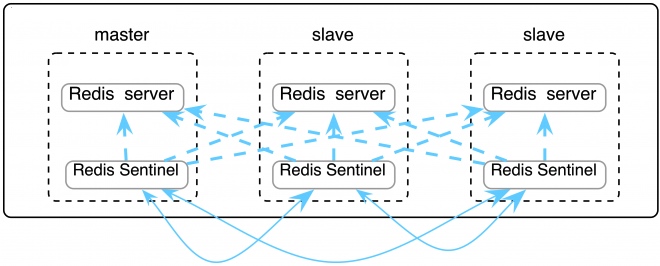
# Redis Sentinel 集群部署
# 概述
Redis 集群可以在一组 redis 节点之间实现高可用性和 sharding。在集群中会有 1 个 master 和多个 slave 节点。当 master 节点失效时,应选举出一个 slave 节点作为新的 master。然而 Redis 本身(包括它的很多客户端)没有实现自动故障发现并进行主备切换的能力,需要外部的监控方案来实现自动故障恢复。
Redis Sentinel 是官方推荐的高可用性解决方案。它是 Redis 集群的监控管理工具,可以提供节点监控、通知、自动故障恢复和客户端配置发现服务。
# Redis Sentinel 核心配置
# Example sentinel.conf
# *** IMPORTANT ***
#
# By default Sentinel will not be reachable from interfaces different than
# localhost, either use the 'bind' directive to bind to a list of network
# interfaces, or disable protected mode with "protected-mode no" by
# adding it to this configuration file.
#
# Before doing that MAKE SURE the instance is protected from the outside
# world via firewalling or other means.
#
# For example you may use one of the following:
#
# bind 127.0.0.1 192.168.1.1
#
# protected-mode no
# port <sentinel-port>
# The port that this sentinel instance will run on
port 26379
# sentinel announce-ip <ip>
# sentinel announce-port <port>
#
# The above two configuration directives are useful in environments where,
# because of NAT, Sentinel is reachable from outside via a non-local address.
#
# When announce-ip is provided, the Sentinel will claim the specified IP address
# in HELLO messages used to gossip its presence, instead of auto-detecting the
# local address as it usually does.
#
# Similarly when announce-port is provided and is valid and non-zero, Sentinel
# will announce the specified TCP port.
#
# The two options don't need to be used together, if only announce-ip is
# provided, the Sentinel will announce the specified IP and the server port
# as specified by the "port" option. If only announce-port is provided, the
# Sentinel will announce the auto-detected local IP and the specified port.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel announce-ip 1.2.3.4
# dir <working-directory>
# Every long running process should have a well-defined working directory.
# For Redis Sentinel to chdir to /tmp at startup is the simplest thing
# for the process to don't interfere with administrative tasks such as
# unmounting filesystems.
dir /tmp
# sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum>
#
# Tells Sentinel to monitor this master, and to consider it in O_DOWN
# (Objectively Down) state only if at least <quorum> sentinels agree.
#
# Note that whatever is the ODOWN quorum, a Sentinel will require to
# be elected by the majority of the known Sentinels in order to
# start a failover, so no failover can be performed in minority.
#
# Slaves are auto-discovered, so you don't need to specify slaves in
# any way. Sentinel itself will rewrite this configuration file adding
# the slaves using additional configuration options.
# Also note that the configuration file is rewritten when a
# slave is promoted to master.
#
# Note: master name should not include special characters or spaces.
# The valid charset is A-z 0-9 and the three characters ".-_".
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
# sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>
#
# Set the password to use to authenticate with the master and slaves.
# Useful if there is a password set in the Redis instances to monitor.
#
# Note that the master password is also used for slaves, so it is not
# possible to set a different password in masters and slaves instances
# if you want to be able to monitor these instances with Sentinel.
#
# However you can have Redis instances without the authentication enabled
# mixed with Redis instances requiring the authentication (as long as the
# password set is the same for all the instances requiring the password) as
# the AUTH command will have no effect in Redis instances with authentication
# switched off.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel auth-pass mymaster MySUPER--secret-0123passw0rd
# sentinel down-after-milliseconds <master-name> <milliseconds>
#
# Number of milliseconds the master (or any attached slave or sentinel) should
# be unreachable (as in, not acceptable reply to PING, continuously, for the
# specified period) in order to consider it in S_DOWN state (Subjectively
# Down).
#
# Default is 30 seconds.
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
# sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <numslaves>
#
# How many slaves we can reconfigure to point to the new slave simultaneously
# during the failover. Use a low number if you use the slaves to serve query
# to avoid that all the slaves will be unreachable at about the same
# time while performing the synchronization with the master.
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
# sentinel failover-timeout <master-name> <milliseconds>
#
# Specifies the failover timeout in milliseconds. It is used in many ways:
#
# - The time needed to re-start a failover after a previous failover was
# already tried against the same master by a given Sentinel, is two
# times the failover timeout.
#
# - The time needed for a slave replicating to a wrong master according
# to a Sentinel current configuration, to be forced to replicate
# with the right master, is exactly the failover timeout (counting since
# the moment a Sentinel detected the misconfiguration).
#
# - The time needed to cancel a failover that is already in progress but
# did not produced any configuration change (SLAVEOF NO ONE yet not
# acknowledged by the promoted slave).
#
# - The maximum time a failover in progress waits for all the slaves to be
# reconfigured as slaves of the new master. However even after this time
# the slaves will be reconfigured by the Sentinels anyway, but not with
# the exact parallel-syncs progression as specified.
#
# Default is 3 minutes.
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
# SCRIPTS EXECUTION
#
# sentinel notification-script and sentinel reconfig-script are used in order
# to configure scripts that are called to notify the system administrator
# or to reconfigure clients after a failover. The scripts are executed
# with the following rules for error handling:
#
# If script exits with "1" the execution is retried later (up to a maximum
# number of times currently set to 10).
#
# If script exits with "2" (or an higher value) the script execution is
# not retried.
#
# If script terminates because it receives a signal the behavior is the same
# as exit code 1.
#
# A script has a maximum running time of 60 seconds. After this limit is
# reached the script is terminated with a SIGKILL and the execution retried.
# NOTIFICATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel notification-script <master-name> <script-path>
#
# Call the specified notification script for any sentinel event that is
# generated in the WARNING level (for instance -sdown, -odown, and so forth).
# This script should notify the system administrator via email, SMS, or any
# other messaging system, that there is something wrong with the monitored
# Redis systems.
#
# The script is called with just two arguments: the first is the event type
# and the second the event description.
#
# The script must exist and be executable in order for sentinel to start if
# this option is provided.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh
# CLIENTS RECONFIGURATION SCRIPT
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script <master-name> <script-path>
#
# When the master changed because of a failover a script can be called in
# order to perform application-specific tasks to notify the clients that the
# configuration has changed and the master is at a different address.
#
# The following arguments are passed to the script:
#
# <master-name> <role> <state> <from-ip> <from-port> <to-ip> <to-port>
#
# <state> is currently always "failover"
# <role> is either "leader" or "observer"
#
# The arguments from-ip, from-port, to-ip, to-port are used to communicate
# the old address of the master and the new address of the elected slave
# (now a master).
#
# This script should be resistant to multiple invocations.
#
# Example:
#
# sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
# SECURITY
#
# By default SENTINEL SET will not be able to change the notification-script
# and client-reconfig-script at runtime. This avoids a trivial security issue
# where clients can set the script to anything and trigger a failover in order
# to get the program executed.
sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
# 搭建 Redis 集群
搭建一主两从环境,docker-compose.yml 配置如下:
version: '3.1'
services:
master:
image: redis
container_name: redis-master
ports:
- 6379:6379
slave1:
image: redis
container_name: redis-slave-1
ports:
- 6380:6379
command: redis-server --slaveof redis-master 6379
slave2:
image: redis
container_name: redis-slave-2
ports:
- 6381:6379
command: redis-server --slaveof redis-master 6379
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 搭建 Sentinel 集群
我们至少需要创建三个 Sentinel 服务,docker-compose.yml 配置如下:
version: '3.1'
services:
sentinel1:
image: redis
container_name: redis-sentinel-1
ports:
- 26379:26379
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
volumes:
- ./sentinel1.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
sentinel2:
image: redis
container_name: redis-sentinel-2
ports:
- 26380:26379
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
volumes:
- ./sentinel2.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
sentinel3:
image: redis
container_name: redis-sentinel-3
ports:
- 26381:26379
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
volumes:
- ./sentinel3.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 修改 Sentinel 配置文件
需要三份 sentinel.conf 配置文件,分别为 sentinel1.conf,sentinel2.conf,sentinel3.conf,配置文件内容相同
port 26379
dir /tmp
# 自定义集群名,其中 127.0.0.1 为 redis-master 的 ip,6379 为 redis-master 的端口,2 为最小投票数(因为有 3 台 Sentinel 所以可以设置成 2)
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
sentinel deny-scripts-reconfig yes
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
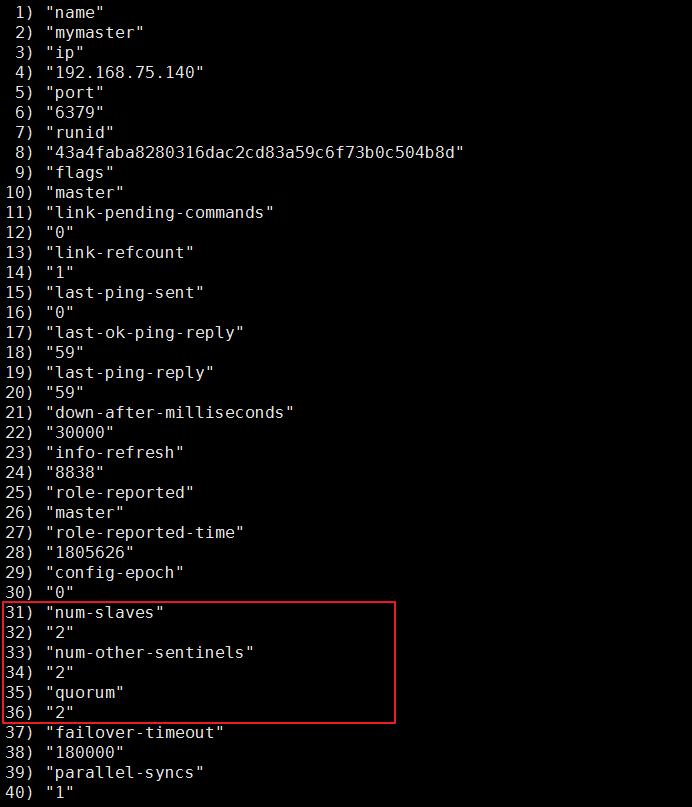
# 查看集群是否生效
进入 Sentinel 容器,使用 Sentinel API 查看监控情况:
docker exec -it redis-sentinel-1 /bin/bash
redis-cli -p 26379
sentinel master mymaster
sentinel slaves mymaster
2
3
4
# Redis 命令汇总
# 参考资料
http://redisdoc.com/ http://redis.io/commands
# 连接操作相关的命令
- ping:测试连接是否存活如果正常会返回 pong
- echo:打印
- select:切换到指定的数据库,数据库索引号 index 用数字值指定,以 0 作为起始索引值
- quit:关闭连接(connection)
- auth:简单密码认证
# 服务端相关命令
- time:返回当前服务器时间
- client list: 返回所有连接到服务器的客户端信息和统计数据 参见 http://redisdoc.com/server/client_list.html
- client kill ip:port:关闭地址为 ip:port 的客户端
- save:将数据同步保存到磁盘
- bgsave:将数据异步保存到磁盘
- lastsave:返回上次成功将数据保存到磁盘的Unix时戳
- shundown:将数据同步保存到磁盘,然后关闭服务
- info:提供服务器的信息和统计
- config resetstat:重置 info 命令中的某些统计数据
- config get:获取配置文件信息
- config set:动态地调整 Redis 服务器的配置(configuration)而无须重启,可以修改的配置参数可以使用命令 CONFIG GET * 来列出
- config rewrite:Redis 服务器时所指定的 redis.conf 文件进行改写
- monitor:实时转储收到的请求
- slaveof:改变复制策略设置 ###发布订阅相关命令
- psubscribe:订阅一个或多个符合给定模式的频道 例如 psubscribe news.* tweet.*
- publish:将信息 message 发送到指定的频道 channel 例如 publish msg "good morning"
- pubsub channels:列出当前的活跃频道 例如 PUBSUB CHANNELS news.i*
- pubsub numsub:返回给定频道的订阅者数量 例如 PUBSUB NUMSUB news.it news.internet news.sport news.music
- pubsub numpat:返回客户端订阅的所有模式的数量总和
- punsubscribe:指示客户端退订所有给定模式。
- subscribe:订阅给定的一个或多个频道的信息。例如 subscribe msg chat_room
- unsubscribe:指示客户端退订给定的频道。
# 对 KEY 操作的命令
- exists(key):确认一个 key 是否存在
- del(key):删除一个 key
- type(key):返回值的类型
- keys(pattern):返回满足给定 pattern 的所有 key
- randomkey:随机返回 key 空间的一个
- keyrename(oldname, newname):重命名 key
- dbsize:返回当前数据库中 key 的数目
- expire:设定一个 key 的活动时间(s)
- ttl:获得一个 key 的活动时间
- move(key, dbindex):移动当前数据库中的 key 到 dbindex 数据库
- flushdb:删除当前选择数据库中的所有 key
- flushall:删除所有数据库中的所有 key
# 对 String 操作的命令
- set(key, value):给数据库中名称为 key 的 string 赋予值 value
- get(key):返回数据库中名称为 key 的 string 的 value
- getset(key, value):给名称为 key 的 string 赋予上一次的 value
- mget(key1, key2,…, key N):返回库中多个 string 的 value
- setnx(key, value):添加 string,名称为 key,值为 value
- setex(key, time, value):向库中添加 string,设定过期时间 time
- mset(key N, value N):批量设置多个 string 的值
- msetnx(key N, value N):如果所有名称为 key i 的 string 都不存在
- incr(key):名称为 key 的 string 增 1 操作
- incrby(key, integer):名称为 key 的 string 增加 integer
- decr(key):名称为 key 的 string 减 1 操作
- decrby(key, integer):名称为 key 的 string 减少 integer
- append(key, value):名称为 key 的 string 的值附加 value
- substr(key, start, end):返回名称为 key 的 string 的 value 的子串
# 对 List 操作的命令
- rpush(key, value):在名称为 key 的 list 尾添加一个值为 value 的元素
- lpush(key, value):在名称为 key 的 list 头添加一个值为 value 的元素
- llen(key):返回名称为 key 的 list 的长度
- lrange(key, start, end):返回名称为 key 的 list 中 start 至 end 之间的元素
- ltrim(key, start, end):截取名称为 key 的 list
- lindex(key, index):返回名称为 key 的 list 中 index 位置的元素
- lset(key, index, value):给名称为 key 的 list 中 index 位置的元素赋值
- lrem(key, count, value):删除 count 个 key 的 list 中值为 value 的元素
- lpop(key):返回并删除名称为 key 的 list 中的首元素
- rpop(key):返回并删除名称为 key 的 list 中的尾元素
- blpop(key1, key2,… key N, timeout):lpop 命令的 block 版本。
- brpop(key1, key2,… key N, timeout):rpop 的 block 版本。
- rpoplpush(srckey, dstkey):返回并删除名称为 srckey 的 list 的尾元素,并将该元素添加到名称为 dstkey 的 list 的头部
# 对 Set 操作的命令
- sadd(key, member):向名称为 key 的 set 中添加元素 member
- srem(key, member) :删除名称为 key 的 set 中的元素 member
- spop(key) :随机返回并删除名称为 key 的 set 中一个元素
- smove(srckey, dstkey, member) :移到集合元素
- scard(key) :返回名称为 key 的 set 的基数
- sismember(key, member) :member 是否是名称为 key 的 set 的元素
- sinter(key1, key2,…key N) :求交集
- sinterstore(dstkey, (keys)) :求交集并将交集保存到 dstkey 的集合
- sunion(key1, (keys)) :求并集
- sunionstore(dstkey, (keys)) :求并集并将并集保存到 dstkey 的集合
- sdiff(key1, (keys)) :求差集
- sdiffstore(dstkey, (keys)) :求差集并将差集保存到 dstkey 的集合
- smembers(key) :返回名称为 key 的 set 的所有元素
- srandmember(key) :随机返回名称为 key 的 set 的一个元素
# 对 Hash 操作的命令
- hset(key, field, value):向名称为 key 的 hash 中添加元素 field
- hget(key, field):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中 field 对应的 value
- hmget(key, (fields)):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中 field i 对应的 value
- hmset(key, (fields)):向名称为 key 的 hash 中添加元素 field
- hincrby(key, field, integer):将名称为 key 的 hash 中 field 的 value 增加 integer
- hexists(key, field):名称为 key 的 hash 中是否存在键为 field 的域
- hdel(key, field):删除名称为 key 的 hash 中键为 field 的域
- hlen(key):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中元素个数
- hkeys(key):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中所有键
- hvals(key):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中所有键对应的 value
- hgetall(key):返回名称为 key 的 hash 中所有的键(field)及其对应的 value
# Redis Sentinel
- ping :返回 pong
- sentinel masters :列出所有被监视的主服务器,以及这些主服务器的当前状态。
- sentinel slaves:列出给定主服务器的所有从服务器,以及这些从服务器的当前状态。
- sentinel get-master-addr-by-name:返回给定名字的主服务器的 IP 地址和端口号。如果这个主服务器正在执行故障转移操作,或者针对这个主服务器的故障转移操作已经完成,那么这个命令返回新的主服务器的 IP 地址和端口号。
- sentinel reset:重置所有名字和给定模式 pattern 相匹配的主服务器。pattern 参数是一个 Glob 风格的模式 重置操作清楚主服务器目前的所有状态,包括正在执行中的故障转移,并移除目前已经发现和关联的,主服务器的所有从服务器和 Sentinel 。
- sentinel failover:当主服务器失效时,在不询问其他 Sentinel 意见的情况下,强制开始一次自动故障迁移(不过发起故障转移的 Sentinel 会向其他 Sentinel 发送一个新的配置,其他 Sentinel 会根据这个配置进行相应的更新)。